DEFC: simple enumeration tool for detect AV/EDR
Hello, cybersecurity enthusiasts and white hackers!
This post is the result of our research and the result on the pentest practical cases. We just show the basic Proof of Concept code which detect AV/EDR engine in Windows machine.
research
First of all, let’s say we have a file with this format:
acctmgr.exe|Symantec
AcctMgr.exe|Symantec
ashSimpl.exe|Avast
ashSkPcc.exe|Avastavpcc.exe|Kaspersky
AVPDTAgt.exe|Kaspersky Lab Deployment Tool Agent
avpexec.exe|Kaspersky
avp.exe|Kaspersky
...
Let’s go to define some struct:
// define a struct to store process name and description
typedef struct {
char process_name[256];
char description[256];
} Process;
// array of Process structs, and counter
Process* process_list;
int process_count = 0;
And read process list from this file:
// read process data from a file
void readProcListFromFile(const char* filename) {
FILE* file = fopen(filename, "r");
if (file == NULL) {
printf("Could not open file %s", filename);
return;
}
char line[512];
while (fgets(line, sizeof(line), file)) {
// reallocate memory for each new process
process_list = (Process*)realloc(process_list, (process_count + 1) * sizeof(Process));
// parse the line, split it into process name and description
char* token = strtok(line, "|");
strcpy(process_list[process_count].process_name, token);
token = strtok(NULL, "|");
strcpy(process_list[process_count].description, token);
process_count++;
}
fclose(file);
}
Then, we just check the running processes in the system, for example microsoft provides a good example of how to do this.
// enumerate running processes
void enumProcs() {
HANDLE hProcessSnap;
PROCESSENTRY32 pe32;
hProcessSnap = CreateToolhelp32Snapshot(TH32CS_SNAPPROCESS, 0);
if (hProcessSnap == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE) {
printf("CreateToolhelp32Snapshot failed.\n");
return;
}
pe32.dwSize = sizeof(PROCESSENTRY32);
if (!Process32First(hProcessSnap, &pe32)) {
printf("Process32First failed.\n");
CloseHandle(hProcessSnap);
return;
}
do {
for (int i = 0; i < process_count; i++) {
if (_stricmp(process_list[i].process_name, pe32.szExeFile) == 0) {
printf("found process: %s - %s \n", process_list[i].process_name, process_list[i].description);
}
}
} while (Process32Next(hProcessSnap, &pe32));
CloseHandle(hProcessSnap);
}
The only difference is if we found process from list, just print it.
That’s all!
demo
Let’s go to see everything in action.
Compile it in attacker’s machine via mingw:
x86_64-w64-mingw32-g++ -O2 hack.c -o hack.exe -I/usr/share/mingw-w64/include/ -s -ffunction-sections -fdata-sections -Wno-write-strings -fno-exceptions -fmerge-all-constants -static-libstdc++ -static-libgcc -fpermissive
Then, run it in the victim’s Windows host:
.\hack.exe
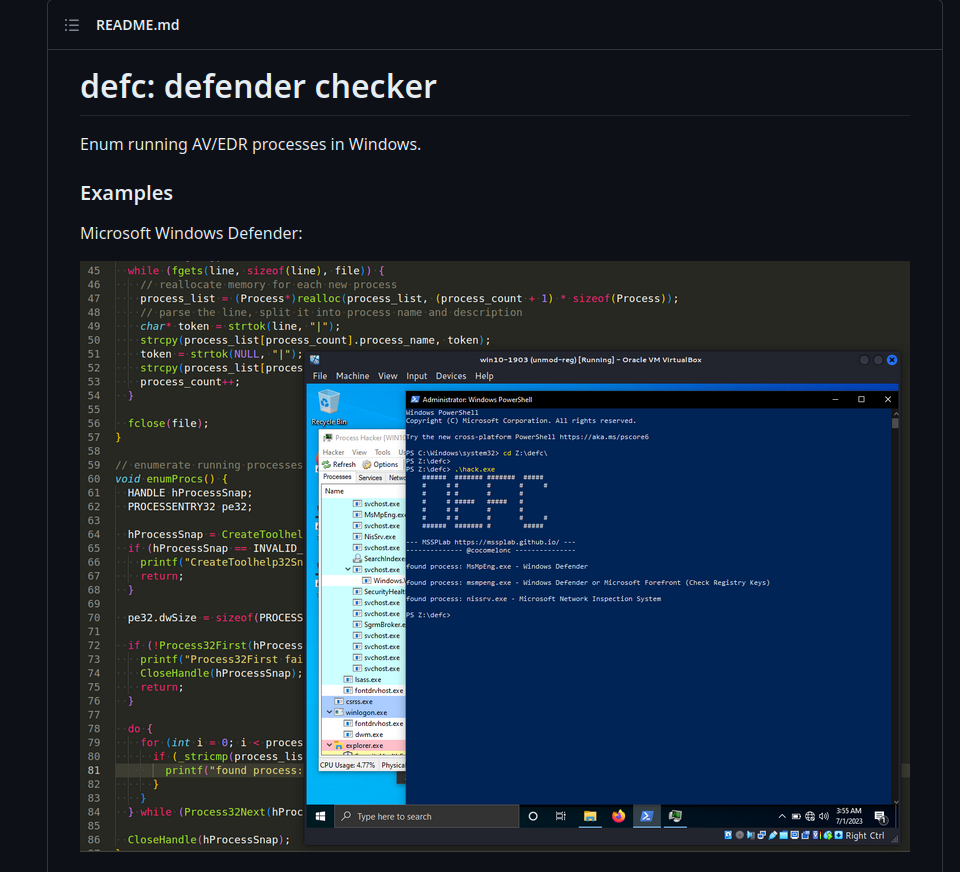
Microsoft Windows Defender:
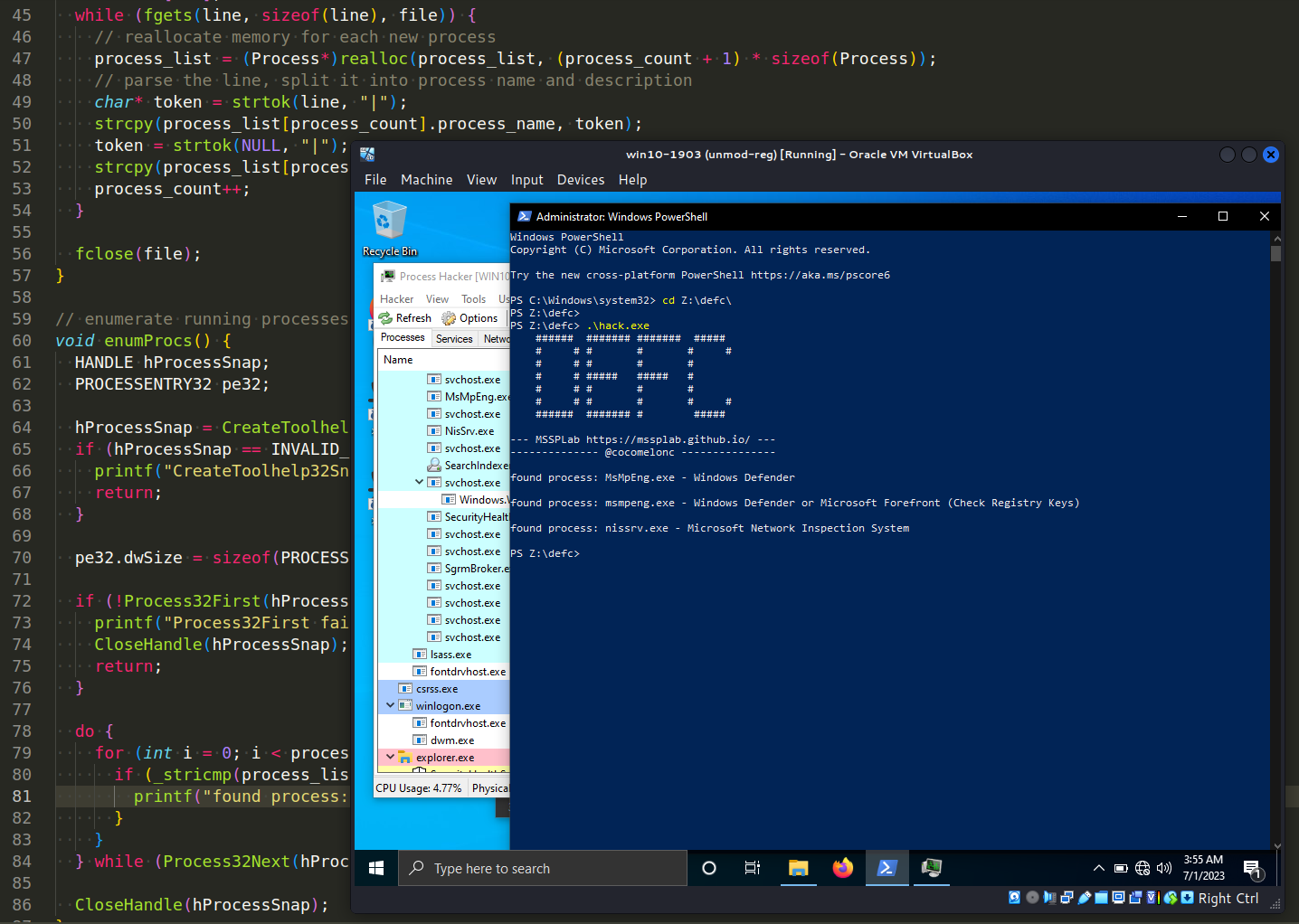
Bitdefender:
Kaspersky Total Security:
As you can see, everything is worked perfectly! =^..^=
As result, we create simple open-source tool defc
https://websec.nl/scanner/result/DQEXTZPBJPRAALEFTWSGYQIGUAFCUP
We hope that this simple tool can help red teamers and pentesters for their enumeration purposes on compromised hosts and serve as a starting point for more their own advanced tools.
By Purple Team from MSSPLab:
References
Find process ID by name and inject to it. Simple C++ example.
Taking a Snapshot and Viewing Processes
source code in github
Thanks for your time happy hacking and good bye!
All drawings and screenshots are MSSPLab’s